What is a Piezo Buzzer: Benefits, How to Use it & How it Works

Piezo Buzzers
Piezo buzzers are compact electronic devices used to produce audible alerts or notifications. They operate based on the piezoelectric effect, a property that allows certain materials to generate an electric charge under mechanical stress. This unique characteristic has made piezo buzzers popular in diverse applications, from household appliances to medical equipment and industrial machinery.
At FHD Manufacturing, we offer a wide range of piezo buzzers, catering to different sizes, frequencies, and sound outputs. Whether you need self-oscillating buzzers with signal generators or cost-effective options without signal generators, our diverse selection of piezo buzzers is designed to meet your specific requirements.
Benefits of FHD’s Piezo Buzzers
FHD’s piezo buzzers offer several advantages:
- Variety in Size, Frequency, and Sound Output: Our piezo buzzers, with customizable sound outputs, come in various sizes and frequencies. Whether you require self-oscillating buzzers, multi-tone sound generators, or sirens, we have the solution for you at competitive prices.
- Efficient Circuitry: Our piezo buzzers feature built-in circuitry, ensuring easy integration and low power consumption, making them cost-effective for your applications.
- Non-Magnetic Construction: With non-magnetic construction, our piezo buzzers are versatile and can be easily mounted on printed circuit boards, enhancing their adaptability to different environments.
- Swift Delivery: We understand the importance of timing. With FHD Products, you can expect fast delivery, ensuring your projects stay on track.
Applications of FHD’s Piezo Buzzers
From simple beeps to loud alarms, an FHD piezo buzzer is ideal for your audio alert needs. Our buzzers find applications in various industries, including:
- Microwave Ovens
- MRI Suites
- White Goods
- IoT Devices
- Diabetes Meters
- Doorbells
- Smoke Alarms
- Pet Training Devices
- Defibrillators
- Toys and Games
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms
- Automotive Instrumentation
Exploring FHD's Piezo Buzzer Lineup
Below is our piezo buzzer lineup. Explore our range of piezo buzzer products to discover their incredible versatility and customization options. Whether you need a buzzer tailored to your specific requirements or a perfect piezo buzzer solution, our products can deliver the precision and performance you demand:
|
Model Number |
Image |
Dimensions (mm) in Ø x H |
Resonance Frequency (Hz) |
Operating Voltage
(VDC ) |
Min. Sound Pressure Level @ 12VDC (dB) |
Operating Temperature (℃ ) |
Tone |
Application |
Specification |
|
|
23.3 x 9.5 |
3200±500 |
6 ~ 15 |
95 |
-20~70 | Continuous | Security System | ||
 |
23.3 x 16.0 |
3400±500 |
5 ~ 15 |
85 |
-20~70 | Continuous | Security System | ||
 |
23.7 x 9.5 |
3500±500 |
15 ~ 28 |
95 |
-20~70 | Continuous | Security System | ||
 |
29.5 x 24.3 |
3500±500 |
6 ~ 15 |
95 |
-20~70 | Continuous | Security System | ||
|
43.0 x 12.2 |
2800±500 |
4~ 20 |
100 |
-20~60 | Continuous | Engineering Vehicle Reversing System | |||
 |
23.3 x 9.5 |
3200 ± 500 |
6 ~ 15 |
95 | -20~70 | Continuous | Security System | ||
 |
22.8 x 11.6 |
3500 ± 500 |
8 ~ 15 |
95 | -40~80 | Continuous | Security System | ||
 |
36.0 x 30.5 |
2800±500 |
6 ~ 15 |
90 | -20~70 | Slow Pulse | Golf Cart | ||
 |
36.0 x 30.5 |
2800±500 |
9 ~ 48 |
100 | -20~70 | Synth Sound | Golf Cart | ||
 |
29.5 x 24.3 |
3500±500 |
6 ~ 15 |
95 | -20~70 | Continuous | Tire Pressure Monitoring |
FHD Electronic Corporation is a prominent electric buzzer manufacturer, renowned for our exceptional customer service and unwavering dedication to top-notch quality. Moreover, we provide warehousing and repackaging services, making us your all-in-one solution for buzzer-related needs and an essential collaborator throughout the entire buzzer manufacturing and sales journey. At FHD Electronic Corporation, our commitment lies in delivering buzzer solutions perfectly tailored to your specific requirements. If you're ready to initiate a project or require further assistance, please don't hesitate to contact us at +1-469-409-2828, email sales@fhdmfg.com, or complete our inquiry form today.
What is a Piezo Buzzer?
A piezo buzzer is a versatile electronic audio device used in various applications, including alarms, doorbells, musical instruments, and toys. It operates on the principle of the piezoelectric effect, which allows certain materials like quartz and ceramics to generate an electrical charge when subjected to mechanical stress or, conversely, to vibrate when an electrical charge is applied.
In a piezo buzzer, a thin piezoelectric disc is sandwiched between two metal plates. When a voltage is applied to these plates, the disc vibrates, producing an audible sound. Piezo buzzers come in different shapes and sizes, offering a range of frequencies and sound levels. Some models even include built-in drivers and control circuits for ease of use.
Piezo buzzers are reliable and cost-effective solutions for generating audio signals in various electronic applications due to their unique properties.
Piezo Buzzer Structure
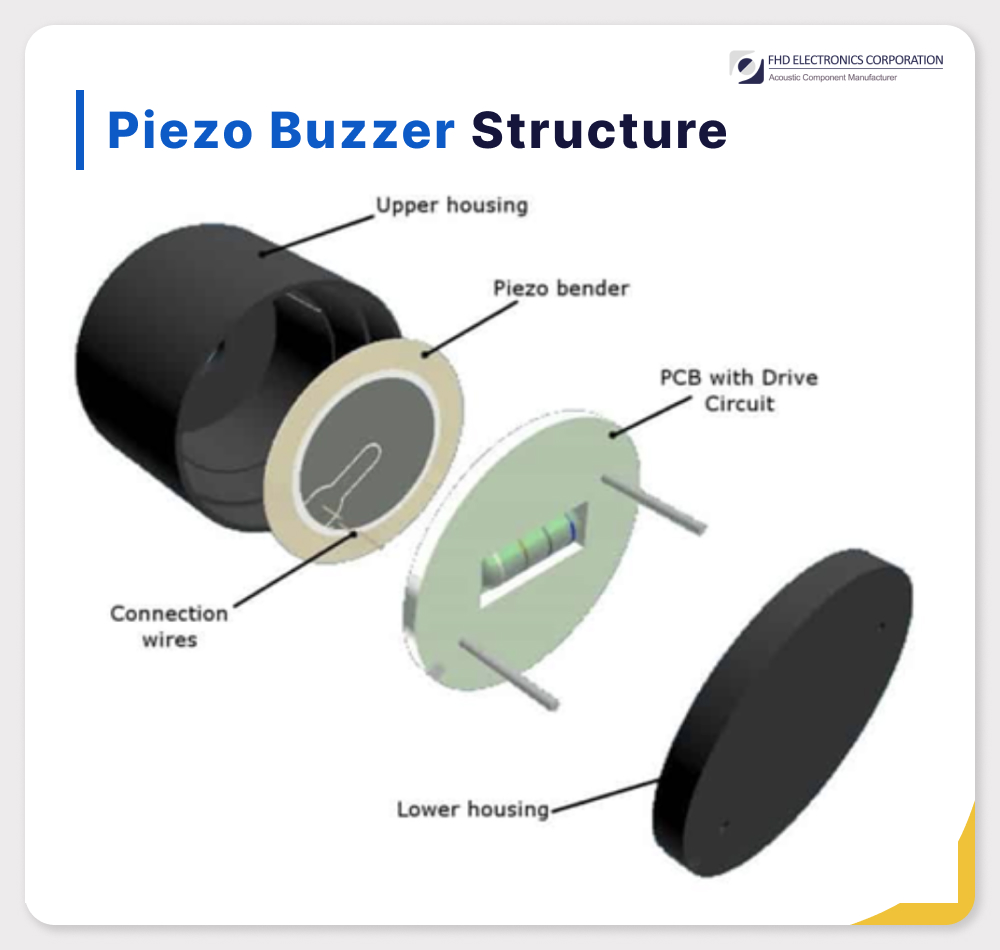
The structure of a piezo buzzer is relatively straightforward but efficient, consisting of key components:
- Piezoelectric Disc: Typically made of specialized ceramic material like lead zirconate titanate (PZT), this disc generates sound waves when subjected to an electric field, causing mechanical vibrations.
- Metal Plates: These plates, often made of brass or stainless steel, serve as electrodes to transmit the electric signal to the piezoelectric material. Their size and shape can vary based on the buzzer's size and output.
- Housing: Some piezo buzzers include housing, often plastic or metal, to protect the components from damage. The housing's design depends on the intended use of the buzzer.
Certain piezo buzzers may also incorporate additional components like drivers or control circuits for regulating sound output in various applications.
How Does a Piezo Buzzer Work?
Piezo buzzers operate based on the piezoelectric effect, which allows specific materials to generate an electric charge under mechanical stress. This effect enables piezo buzzers to convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations and produce sound.
Here's how a piezo buzzer works:
- A thin piezoelectric disc is placed between two metal plates.
- When a voltage is applied to the metal plates, the piezoelectric disc deforms, causing mechanical vibrations.
- These vibrations cause a resonating membrane to vibrate and produce sound waves.
- Electrodes attached to the piezoelectric disc facilitate voltage application and vibration.
The size and shape of the piezoelectric disc and resonating membrane can affect the frequency and intensity of the sound produced by the buzzer. Thinner discs produce higher-frequency sounds, while thicker discs yield lower frequencies. The resonating membrane's shape and size can also be adjusted to produce different sound types.
How to Utilize Piezoelectric Buzzers
The use of piezo ceramic buzzers is based on an inversion of the piezoelectricity principle discovered by Jacques and Pierre Curie in 1880. They found that specific materials could generate electricity under mechanical pressure and, conversely, mechanical movement when exposed to an electric field.
In piezo buzzers, when certain piezoelectric materials encounter an alternating electric field, the piezo buzzer element, typically made of synthetic piezoceramic material, undergoes sequential stretching and compression in sync with the electrical frequency. This results in the emission of an audible sound.
Compared to magnetic buzzers, which generally operate within a voltage range of one to 16 volts, piezo buzzers have a broader operating spectrum, spanning from three to 250 volts. Additionally, magnetic buzzers consume more power, typically ranging from 30 to 100 milliamperes, whereas piezo buzzers typically require less than 30 milliamperes, even at higher frequencies. It's important to note that piezo buzzers may have a larger physical footprint than magnetic buzzers but offer higher sound pressure levels.
Applications of Piezo Buzzers
Piezo buzzers find applications in a wide range of industries. They are commonly used in alarm systems due to their loud, attention-grabbing, high-pitched sounds. Typical applications include smoke detectors, security systems, and emergency alerts.
Electronic devices requiring audible indicators, such as medical equipment, vending machines, and home appliances, also utilize small piezo buzzers for their compact size and low power consumption.
Larger piezo buzzers are employed in industrial settings where louder and more powerful sounds are needed. Conversely, smaller piezo buzzers suit consumer electronics, where size and power efficiency are essential factors. Piezo buzzers can be customized by altering size, shape, and sound frequency to meet specific application requirements.
Audible Sound Transducers
Piezoelectric audible sound transducers, also known as tone generators or buzzers, are prized for their simplicity, compactness, and reliability. These devices can produce high-volume sound output with minimal energy consumption, typically in the milliwatt range. They are employed in various battery-powered equipment, including timers, smoke alarms, games, telephone ringers, metal detectors, watches, car alarms, and more.
The core component of most audible sound transducers comprises a thin piezoelectric ceramic disk bonded to a similarly thin metal diaphragm. Applying an electrical voltage to the ceramic disk causes it to deform, leading to bending of the metal diaphragm. With a recurring voltage, this ceramic-metal assembly vibrates at the same frequency as the applied voltage, resulting in audible sound production. Achieving resonance frequency is crucial, as the ceramic element alone has a frequency too high to produce audible sound, necessitating the inclusion of the metal diaphragm.
The design and construction of piezoelectric ceramic buzzers significantly impact their sound level and cost. Nodal support mounting, which minimizes mechanical constraints, allows for the highest vibration amplitude. However, sound interference from the periphery can occur, necessitating housing to absorb peripheral output.
Clamped edge mounting enables phase synchronization but reduces vibration amplitude due to increased interaction between the element and housing. Flexible edge mounting lowers resonance frequency but requires precise construction for optimal performance.
In summary, the choice of mounting method affects resonance frequency, sound level, uniformity, and cost of piezo buzzers. Nodal support mounting is ideal for self-driven, high-output applications with interference management. Clamped edge mounting offers phase synchronization with reduced vibration amplitude, while flexible edge mounting excels in signal characteristics with careful construction. Center support mounting is the least favored option.
For more information on piezo buzzers, please contact us at +1-469-409-2828, email sales@fhdmfg.com, or complete our inquiry form today.
Reference:
- https://www.engineersgarage.com/piezo-buzzer/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/piezoelectric-disk
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/materials-science/piezoelectricity
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/materials-science/lead-zirconate-titanate
- https://www.americanpiezo.com/standard-products/buzzers.html
Related Articles Suggested for You:
Understanding MEMS Microphone Technology: 2023 Audio Revolution
Buzzers to Know: Magnetic Buzzers VS. Piezo Buzzers

